Section 0: Module Objectives or Competencies
| Course Objective or Competency | Module Objectives or Competency |
|---|---|
| The student will be able to list and explain the objectives and outcomes of the feasibility study for the selection of system projects, and understand the importance of economic, operational, and technical feasibility. | Students will be able to explain why requests are made for system development projects. |
| Students will be able to list and explain the criteria for evaluating project requests. | |
| Students will be able to assess the feasibility of the economic, operational, and technical aspects of a requested project. | |
| Students will be able to explain the process involved in the feasibility study, including assessing the key elements of feasibility using tools like the feasibility impact grid and cost-benefit analysis. |
Section 1: Selection of Systems Projects
Motivation
Many possible drivers exist including:
- Automating a process
- Speeding up a process
- Streamlining a process
- Combining processes
- Reducing errors in input
- Reducing redundant storage
- Reducing redundant output
- Improving system and subsystem integration
Criteria
- Backing from management – absolutely nothing can be accomplished without the endorsement of the people who eventually will foot the bill.
- Appropriate timing of project commitment – can a time commitment be made for installation of new systems or improvement to existing ones.
- Possibility of improving attainment of organizational goals – the project should put the organization on target, not deter it from its goals.
- Practical in terms of resources for the system analyst and organization – is there expertise and resources to carry out the project.
- Worthwhile project compared with other ways the organization could invest resources – when a business commits to one project it is committing resources that are unavailable for other projects.
Section 2: Feasibility Study
A feasibility study will provide management with facts that will aid in determining whether to conduct a full systems study, because judging the feasibility of a proposed systems project is seldom an unambiguous decision.
Objectives
- To determine what's wrong with the current system.
- To determine if a new system should be developed or the current system updated (depends on the extent of the problems with the current system).
- To determine if the proposed system is viable (useful, effective, feasible) for the sponsor.
Outcomes
- an estimate of the potential benefits of the proposed system
- an estimate of the cost and time for doing a detailed study
- a description of the proposed system in terms of
- its objectives
- its functions
- its estimated cost
Section 3: Process Used in the Feasibility Study
- Analysis of the existing system based upon existing procedures, documents, and observation of the system in operation.
- Interviews of personnel involved.
- Determination of functional requirements.
- Analysis of cost vs. benefit.
- Evaluation of system impact on the organization (recall departmental interaction).
Considerations
- Characteristics of existing system
- Organization structure
- Financial considerations such as how much the organization is losing with the existing system or what expenses could be avoided with the proposed system.
Section 4: Key Elements of Feasibility
A feasibility study assesses the operational, technical, and economic merits of the proposed project.
| The Three Key Elements of Feasibility |
|---|
|
Economic Feasibility Systems analysts' time Cost of systems study Cost of employees' time for study Estimated cost of hardware Cost of packaged software or software development |
|
Operational Feasibility Whether the system will operate when installed Whether the system will be used |
|
Technical Feasibility Add on to present system Technology available to meet users' needs |
Economic Feasibility
- Economic feasibility involves identification of the financial benefits and costs associated with a development project to determine whether value of the investment exceeds the time and cost.
-
Includes:
- Analyst and analyst team time
- Business employee time
- Hardware
- Software
- Software development
- For a project to be feasible, the long-term gains must overshadow the short-term costs, or the system must produce an immediate reduction in operating costs.
Operational Feasibility
- Operational feasibility determines if the human resources are available to operate the system once it has been installed.
-
Users that do not want a new system may prevent it from
becoming operationally feasible.
- If users are satisfied with current system, resistance to implementing a new system will be strong.
- If users are dissatisfied with the current system and have expressed a need for change, chances are that the new system will be used.
Technical Feasibility
- Technical Feasibility assesses whether the current technical resources are sufficient for the new system.
- Can current technical resources be upgraded or augmented to provide the level of technology necessary for the new system.
- If not, is there technology in existence that meets the specifications?
Other Feasibility Concerns
- Scheduling
- Can the project time frame and completion dates meet organizational deadlines?
- Legal and Contractual
- What are legal and contractual ramifications of the proposed system development project?
- Political
- How do key stakeholders view the proposed system?
Section 5: Economic Feasibility
Recall that economic feasibility: is a process of identifying the financial benefits and costs associated with a development project.
- Often referred to as a cost-benefit analysis.
- Project should be reviewed after each SDLC (Systems Development Life Cycle) phase in order to decide whether to continue, redirect, or kill a project.
Project Benefits
Tangible Benefits
Tangible benefits refer to items that can be measured in dollars and with certainty.
Examples include
- reduced personnel expenses
- lower transaction costs
- higher profit margins
Most tangible benefits will fit within the following categories:
- Cost reduction and avoidance
- Error reduction
- Increased flexibility
- Increased speed of activity
- Improvement of management planning and control
- Opening new markets and increasing sales opportunities
Intangible Benefits
Intangible benefits are benefits derived from the creation of an information system that cannot be easily measured in dollars or with certainty.
- May have direct organizational benefits, such as the improvement of employee morale.
- May have broader societal implications, such as the reduction of waste creation or resource consumption.
Intangible benefits can include:
- Competitive necessity
- More timely information
- Improved organizational planning
- Increased organizational flexibility
- Availability of new, better, or more information
- Faster decision making
- More confidence in decision quality
- Improved processing efficiency
- Improved asset utilization
- Improved resource control
- Increased accuracy in clerical operations
- Improved work process that can improve employee morale or customer satisfaction
- Improved social responsibility
Project Costs
Tangible Costs
Tangible costs are costs associated with an information system that can be measured in dollars and with certainty.
IS development tangible costs include:
- Hardware costs
- Labor costs
- Operational costs including employee training and building renovations
Intangible Costs
Intangible costs are costs associated with an information system that cannot be easily measured in terms of dollars or with certainty.
Intangible costs can include:
- Loss of customer goodwill (Recall that acquiring new customers can cost five times more than satisfying and retaining current customers)
- Employee morale
- Operational inefficiency
Cost Frequency
One-time Costs
A one-time cost is a cost associated with project start-up and development or system start-up.
These costs encompass activities such as:
- Systems development
- New hardware and software purchases
- User training
- Site preparation
- Data or system conversion
Recurring Costs
Recurring costs are costs resulting from the ongoing evolution and use of a system.
Examples of these costs include:
- Application software maintenance
- Incremental data storage expenses
- Incremental communications
- New software and hardware leases
- Supplies and other expenses (i.e. paper, forms, data center personnel)
Both one-time and recurring costs can consist of items that are fixed or variable in nature.
- Fixed costs are billed or incurred at a regular interval and usually at a fixed rate.
- Variable costs are items that vary in relation to usage.
Possible Information Systems Costs
- Procurement
- Consulting, equipment, site preparation, capital, management time
- Start-up
- Operating systems, communications installation, personnel hiring, organizational disruption
- Project-related
- Application software, software modification, personnel overhead, training, data analysis, documentation
- Operating
- System maintenance, rental, asset depreciation, operation and planning
Section 6: Technical Feasibility
Recall that technical feasibility refers to the development organization’s ability to construct a proposed system.
The potential consequences of not assessing and managing risks can include the following:
- Failure to attain expected benefits from the project
- Inaccurate project cost estimates
- Inaccurate project duration estimates
- Failure to achieve adequate system performance levels
- Failure to adequately integrate the new system with existing hardware, software, or organizational procedures
Project Risk Assessment Factors
The four primary factors associated with the amount of technical risk on a given project are:
- Project size
- Team size, organizational departments, project duration, programming effort
- Project structure
- New vs. renovated system, resulting organizational changes, management commitment, user perceptions
- The development group’s experience with the application and
technology area
- Familiarity with platform, software, development method, application area, development of similar systems
- The user group’s experience with systems development projects
and the application area
- Familiarity with IS development process, application area, use of similar systems
Four general rules emerged as technical risk assessments:
- Larger projects are riskier than smaller projects.
- A system in which the requirements are easily obtained and highly structured will be less risky than one in which requirements are messy, ill structured, ill defined, or subject to the judgment of an individual.
- The development of a system employing commonly used or standard technology will be less risky than one employing novel or nonstandard technology.
- A project is less risky when the user group is familiar with the systems development process and application area than if unfamiliar.
-
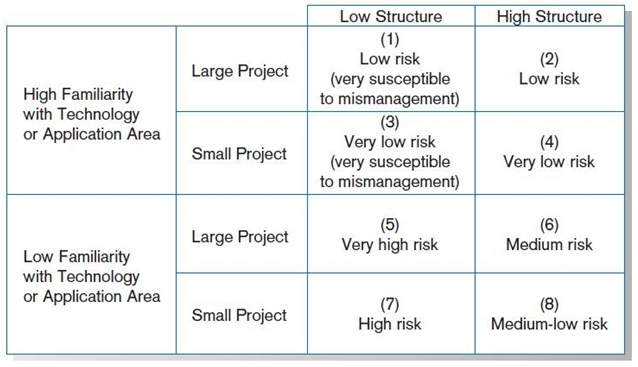
Effects of degree of project structure, project size, and familiarity
with application area on project implementation risk.
Section 7: Feasibility Impact Grid
A Feasibility Impact Grid (FIG) can be used to assess impacts of the development of new systems at both strategic and operational levels.
It can also increase awareness of the impacts made on the achievement of corporate objectives.
In the figures below...
- Current or proposed systems are listed on the left
- Objectives are listed on the top
- Red arrows indicate a positive impact
- Green arrows indicate implementation
By understanding process and corporate objectives, an analyst realizes why he or she is building systems and comprehends what the importance of designing efficient and effective systems might be.
An analyst can use a feasibility impact grid to show how each system component affects process objectives.
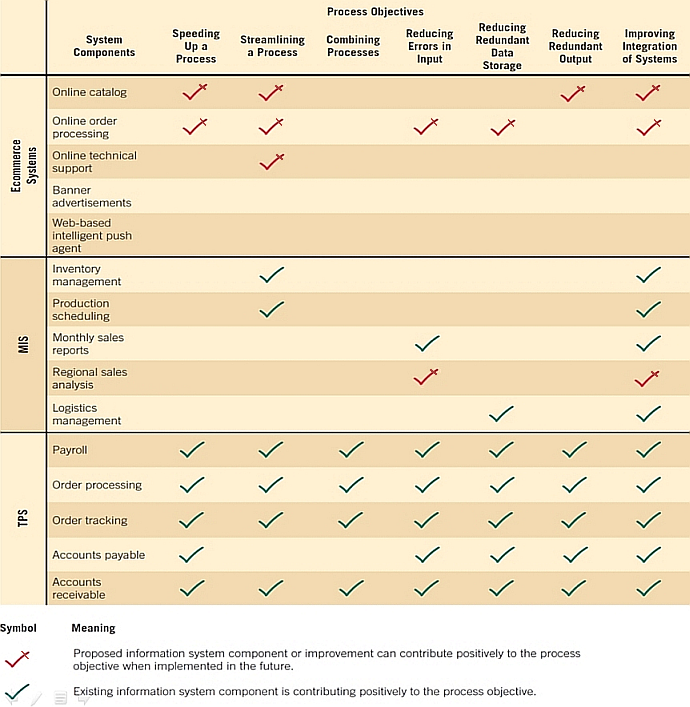
FIG with Process Objectives
An analyst can use a feasibility impact grid to show how each system component affects corporate objectives.
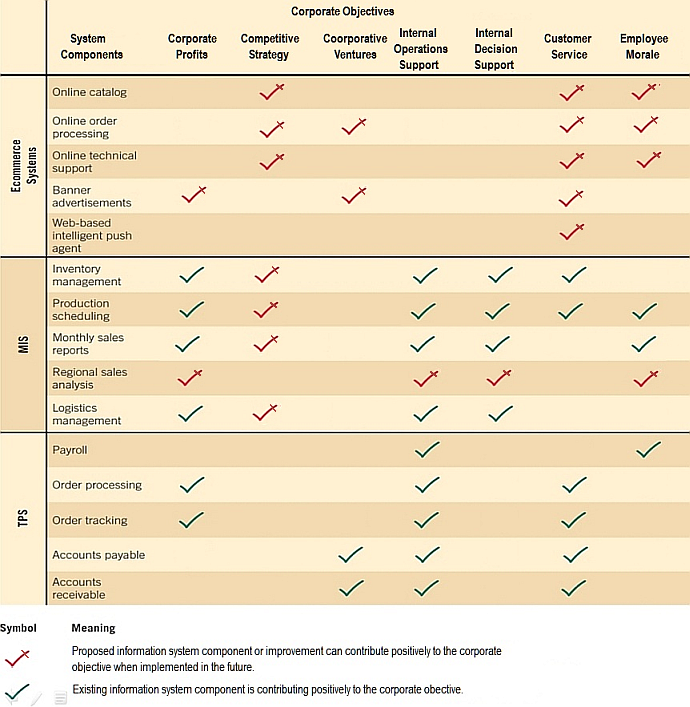
FIG with Corporate Objectives.