Section 0: Module Objectives or Competencies
| Course Objective or Competency | Module Objectives or Competency |
|---|---|
| The student will be introduced to related specializations and techniques for software development. | The student will be able to explain development stacks, like front-end development, back-end development, and full-stack development. |
| The student will be able to explain alternative software development techniques, like CI/CD, DevOps, and 12 Factor Design | |
| The student will be able to explain the Agile software development methodology. |
Section 1: Overview
There is a multitude of specializations and emerging techniques that are too detailed or advanced for a beginning Analysis and Design course, but which students need to be introduced to.
These will be divided into three areas:
- Development Stacks
- Software Development Techniques
- Mobile App Development
- Agile Approaches
Section 2: Development Stacks
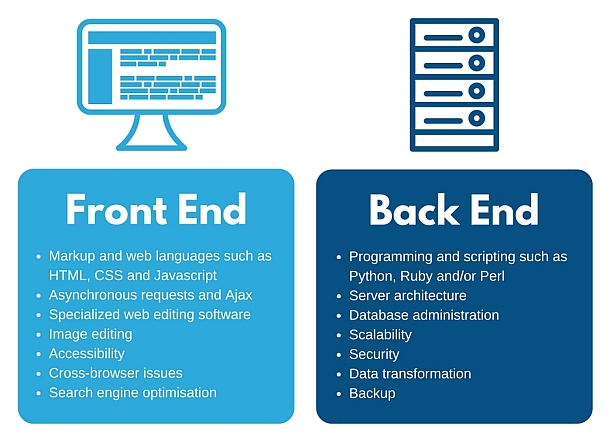
A tech stack is broadly divided into the client side (front end) and server side (back end).
Front-end Developer
Front-end development refers to the client side, that is, a website’s interactive features.
- Front-end developers are responsible for a website’s user-facing code and the architecture of its immersive user experiences.
- Front-end developers work closely with designers or user experience analysts to bring mockups, or wireframes, from development to delivery.
Front-end developers must be adept at three main languages: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript programming.
- In addition to fluency in these languages, front-end developers need to be familiar with frameworks like Bootstrap, Foundation, Backbone, AngularJS, and EmberJS, and libraries like jQuery.
- Front-end development requires a deep and broad understanding of the web development tools and techniques required to develop the web-based application envisioned by the client, as well as significant programming, scripting, and responsive design experience to fully address the intricacies involved in front-end web application development.
- Back-end development requires a deep and broad understanding of the web development tools and techniques required to develop the web-based application envisioned by the client, as well as significant database and programming experience to fully address the intricacies involved in back-end web application development.
Back-end Developer
Back-end development refers to the server-side development.
- Back-end developers primarily develop and maintain the core functional logic and operations of a software application or information system.
- Back-end developers focus on databases, scripting, and the architecture of websites, along with the back-end code that helps to communicate the database information to the browser..
- A back-end developer typically has expert programming skills in Python, Ruby, C#, Java and other high-level programming languages.
Back-end developers also create and maintain the entire back end of a system, which consists of the core application logic, databases, data and application integration, API and other back-end processes.
- The key job role of a back-end developer is to ensure that the data or services requested by the front-end system or software are delivered through programmatic means.
- A back-end developer performs the testing and debugging of any back-end application or system.
- Knowledge of web services and the creation and consumption of REST and SOAP services is helpful.
Full-stack Developer
A full-stack developer can work cross-functionally on the full stack of technology, i.e. both the front end and back end.
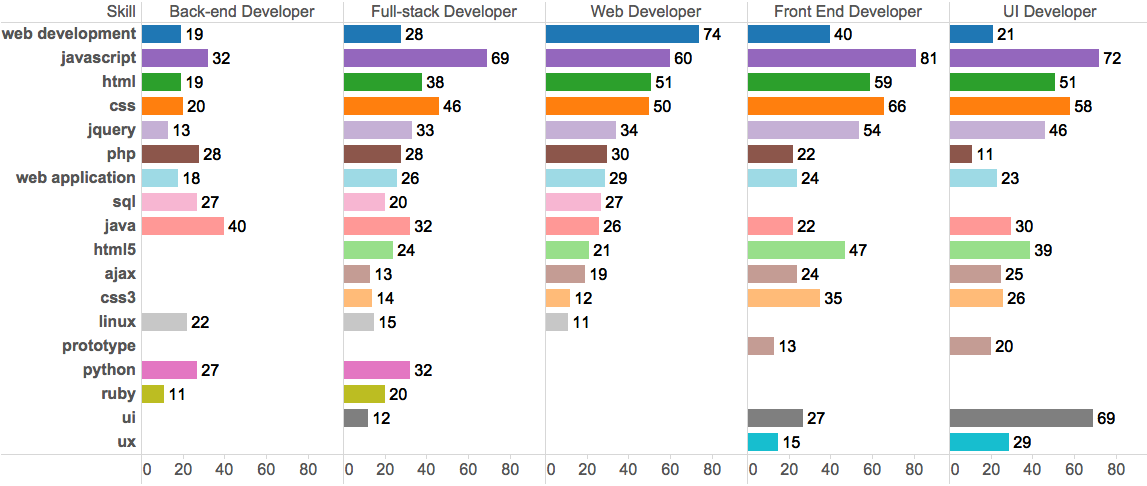
Here are some figures detailing the differences between front-end and back-end developers:

Section 3: Software Development Techniques
A wide variety of software development techniques is available, with DevOps, continuous integration (CI) and continuous deployment (CD), and the 12 Factor Design Methodology becoming more widely used.
CI/CD
Continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) are often cited as pillars of successful DevOps.
- The intent of CI/CD is to improve collaboration between operations and development teams and enable the delivery of high-quality software for continued success.
- CI/CD requires a deep and broad understanding of the software tools and techniques required to develop the system envisioned by the client, as well as significant programming experience to fully understand the constraints involved in terms of such computational resources as space and time.
- Further, CI/CD requires knowledge of not only development, but also about all applications and technologies that interact to make up the software and hardware infrastructure.
DevOps
DevOps is a portmanteau of Development and Operations, and is based on the realization of the value of collaboration between development and operations staff throughout all stages of the development life cycle when creating and operating a software system.
- DevOps involves a set of practices focused on reducing the time between making a change to a system and the change being placed into normal production, while ensuring high quality.
- A DevOps pipeline is a set of automated processes and tools that allows both developers and operations professionals to work cohesively to build and deploy code to a production environment.
- DevOps requires knowledge of not only development, but also about all applications and technologies that interact to make up the software and hardware infrastructure.
12 Factor Apps
12 Factor Apps, sometimes referred to as the 12 Factor Design Methodology, is an app design methodology that was introduced to manage cloud-based apps.
The 12 Factor App methodology is a set of principles that describes a way of making software that, when followed, enables companies to create code that can be released reliably, scaled quickly, and maintained in a consistent and predictable manner.
- The goal is to develop apps for agility and rapid deployment, enabling continuous delivery while being architected to exploit the principles of modern cloud platforms while permitting maximum portability between them along with maximizing scalability.
Section 4: Mobile App Development
A mobile application, commonly referred to as an app, is a type of application software designed to run on a mobile device, such as a smartphone or tablet computer.
- Apps are generally small, individual software units with limited function.
Mobile application development is the process of writing apps, and typically requires experience in languages like HTML5, Swift, and Ionic.
- Developing a mobile app generally involves using a wireframe and/or prototype in which key features, navigation, interaction, and styles are all defined, tested and refined.
- Mobile application development requires an extensive skill set that includes such things as how to fetch data from the Internet and display it, Views and controls, app life cycle, design patterns and development patterns (like Model-View-Controller (MVC), Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM), etc.), multi-threading (with access to UI only on the UI thread), memory management (in a restricted environment), data usage management (caching, etc.), networking (with battery considerations), UI skills like interaction patterns, navigation patterns, native controls and skinning them, creating responsive layouts for various orientations and screen-sizes, etc.
- Mobile devices provide all kinds of sensors and measurements, as well as a variety of network connectivity methods for use in apps, and since a developer cannot know what the state of these sensors or data connections will be when a user fires up the app, additional logic must be added to handle a large number of scenarios.
Progressive Web Applications (PWA)
A progressive web application takes advantage of the latest technologies to combine the best of web and mobile apps. Think of it as a website built using web technologies but that acts and feels like an app.
- Progressive web apps take advantage of the much larger web ecosystem, plug-ins and community and the relative ease of deploying and maintaining a website when compared to a native application in the respective app stores.
Section 5: Agile Approach
The Agile Software Development Methodology is an umbrella term for a set of practices that emphasize close collaboration between the development team and business stakeholders, frequent delivery of business value, tight, self-organizing teams, and smart ways to craft, confirm, and deliver code.
An Overview of Agile Development
- The Agile approach stresses collaboration over documentation, self-organization rather than rigid management practices, and the ability to manage constant change rather than being locked in a rigid development process.
-
Agile makes use of a variety of tools and approaches like user stories, Kanban, pair
programming, extreme programming, sprints, Scrum teams, and code refactoring.
Agile Project Management Frameworks: Scrum, Kanban, Scrumban, Lean, and Extreme Programming (XP)
Agile Methodologies - XP | Kanban | Lean | Scrum | Crystal | DSDM | ASD
Agile Project Management
Project management involves initiating, planning, executing, controlling the work of a team to achieve project goals.
Agile project management focuses on continuous improvement in the development of a product or service.
- Agile project management provides a lightweight process framework that embraces iterative and incremental practices, helping organizations deliver working software more quickly.
- Agile software development relies on a process involving analysis, planning, a design-build-test phase, and a subsequent deployment of an intermediate product that satisfies a growing subset of user requirements.
- Scrum project management is a methodology for managing software delivery that comes under the broader umbrella of Agile project management.
Agile Analysis and Design
The Agile analysis and design approach uses an iterative process to deliver small incremental releases at short and regular intervals known as sprints or iterations.
- Each iteration focuses on the development of a prioritized subset of features through a process involving analysis, planning, a design-build-test phase, and a subsequent deployment of an intermediate product that satisfies only a subset of user requirements.
- The next iteration will add additional features, followed by even more in the next iteration, in an ongoing incremental cycle until a final product with a complete feature set is accepted by the user.
Scrum Master (Agile)
Scrum, according to Scrum.org, is a framework that allows teams to work on complex projects and deliver high-value products by approaching problems adaptively.
The Scrum Master role was created as part of the Scrum framework; the name was initially intended to indicate someone who is an expert at Scrum and can therefore coach others.
- The Scrum Master serves the stakeholders by making sure that the goals, scope, and product domain are clear to everyone on the Development Team.
- The Scrum Master serves the Development Team by not only promoting and supporting Scrum theory, practices, rules, and values as defined in the Scrum Guide, but also by shielding the team from external interference and distractions so the Team is free to focus on the work of producing output that will generate the desired outcome.
- Further, the Scrum Master arranges and facilitates the team’s meetings – Sprint Planning, Daily Scrums, the Sprint Review, the Sprint Retrospective, etc.
- Serving as a Scrum Master requires in depth knowledge of Scrum theory, practices, rules, and values as defined in the Scrum Guide in order to serve as teacher, coach and mentor, facilitator and change agent.
Software Release - Agile
Software release management is the process of managing, planning, scheduling and controlling a software build through different stages and environments, including testing and deploying software releases.
- Release management is a relatively new but rapidly growing discipline within software engineering.
Agile methodologies produce software releases at the end of each iteration.
- In agile software development, a release is a deployable software package that is the culmination of several iterations.
- Each release provides only a subset of user requirements, but the number of features provided increases with every iteration.
- Releases can be made before the end of an iteration.
- To be classified as successful, the release must meet the following objectives: (a) Deployed on time; (b) Deployed on budget; (c) Have no or negligible impact on existing customers; (d) Satisfy the requirements of new customers, competitive pressure and/ or technological advances.
- Software release management involves implementing pipelines by installing, configuring, and integrating corresponding general-purpose deployment automation tooling.
Lectures from another professor
Agile Development
eXtreme Programming
Online Resources
Agile Project Management: Best Practices and Methodologies
Section 6: Closing
The most enchanting aspect of a career in Information Systems or Computer Science is the opportunity to continue learning throughout your life, as no field changes more quickly or inexorably.
The most daunting aspect of a career in Information Systems or Computer Science is the responsibility and the requirement to learn and adapt as these changes take place.