Section 0: Module Objectives or Competencies
| Course Objective or Competency | Module Objectives or Competency |
|---|---|
| The student will be able to explain the need for and relevance of Systems Analysis and Design. | The student will be able to list the tasks for which a systems analyst is responsible. |
| The student will be able to explain how Systems Analysis and Design techniques can be used to reduce the failure rates for software development projects. |
Section 1: Why should we care about System Analysis and Design?
Have you ever complained that the specs for a programming assignment were too vague, not well thought out, or virtually impossible to implement? Were assignments specs ever modified by the professor after you had started an assignment? Why were they written so poorly?
What is needed to improve the assignments? Why are assignments written by Professor X perceived as being more clear than those written by Professor Y? What goes into writing a decent assignment?
In programming classes you have been given specifications for programming assignments, sometimes written very poorly, but still provided in advance. It is difficult to anticipate in advance everything that the student needs to know to complete an assignment.
What’s worse, many programming courses limit student exercises to “toy” problems, a term that is often used to refer to unrealistically easy exercises. How much more complex would assignment specifications be if they were attempting to describe the requirements of an actual system?
One aspect of a systems analyst’s job is developing a requirements specification document. But before beginning to write the document, the analyst must first interact with multiple users to determine what those requirements include, a daunting task in and of itself. Here are some of the tasks for which a systems analyst is responsible (from What does a systems analyst do).
- Interact with the clients to determine their system requirements
- Translate user requirements into technical specifications
- Interact with designers to convey the possible interface of the software
- Interact/guide the coders/developers to keep track of system development
- Perform system testing with sample/live data with the help of testers
- Implement the new system
- Prepare high quality documentation
Section 2: Failure Rates
For the year 2020, the CISQ Consortium for Information & Software Quality's report, The Cost of Poor Software Quality in the US: A 2020 Report determined the total Cost of Poor Software Quality (CPSQ) in the US is $2.08 trillion (T).
They also note that the 2020 US figure for the software technical debt residing in severe defects that need to be corrected would be $1.31 T (minus interest) but did not include technical debt in the total CPSQ since it represents a future cost that is increasing (14% rise since 2018).
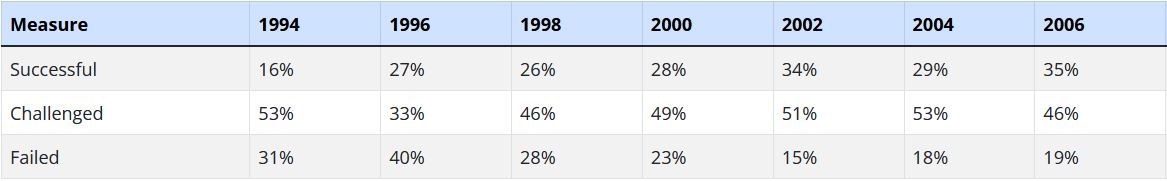
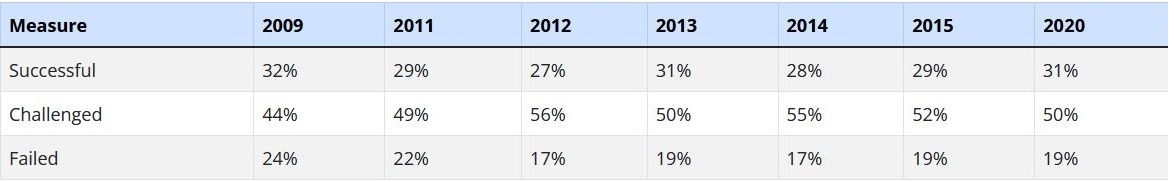
- According to The Standish Group’s Annual CHAOS 2020 report, almost 66% of technology projects (based on the analysis of 50,000 projects globally) end in partial or total failure. While larger projects are more prone to encountering challenges or failing altogether, even the smallest software projects fail one in ten times. Large projects are successful less than 10% of the time.
- Standish also found that 31% of US IT projects were canceled outright and the performance of 53% ‘was so worrying that they were challenged.’
- Research from McKinsey in 2020 found that 17% of large IT projects go so badly, they threaten the very existence of the company.
- A 2020 report from the Boston Consulting Group estimated that 70% of digital transformation efforts fall short of meeting targets.
- A 2020 CISQ report found the total cost of unsuccessful development projects among US firms is an estimated $260B, while the total cost of operational failures caused by poor quality software is estimated at $1.56 trillion.
Here are some past Standish Annual CHAOS Report figures.
Section 3: Software Development Failures
In 2020 the paper 14 Common Reasons Software Projects Fail (And How To Avoid Them) explains various failures encountered in software development:
- Not Understanding The Needs Of The Business
- Inability To Reach Consensus On Priorities
- Lack Of Clarity And Execution Strategy
- Not Starting With The End Customer
- Unclear Requirements
- Expecting A ‘Silver Bullet’
- Expecting A ‘Silver Bullet’
- Thinking That Scope Can Be Defined Upfront
- Lack Of Coordination And Detailed Planning
- Friction Caused By Undefined Roles
- Expecting Overcustomization Of Software
- Lack Of Discipline
- Too Many Hands In The Dev Pot
- Not Enough Emphasis On Soft Skills
Many of these problems can be avoided by keeping a few simple guidelines in mind:
- Keep the users involved throughout the development process.
- Embrace iteration to incorporate features that may have been overlooked or implemented incorrectly due to misunderstandings.
- Do not hesitate to use whatever tools are needed. Hybrid approaches are becoming more common as software developers realize that there is no "one size fits all" approach to software development.
Here is a funny recruiting video for anything but Software Engineering.
Section 4: Systems Analyst
A business professional who uses analysis and design techniques to solve business problems using information technology.
Role of the System Analyst
- A systems analyst studies the problems and needs of a business to determine how people, processes, data, communication, and technology can best accomplish improvements for the business.
- A systems analyst bridges the communication gap between business experts and technology experts.
Skills Needed
- Working knowledge of information technology
- Computer programming experience and expertise
- General business knowledge
- Problem-solving skills
-
Interpersonal communication skills to interact with a variety of stakeholders
- Stakeholders include any group or individual with a vested interest in the system being developed.
- Interpersonal relations skills
- Flexibility and adaptability
- Character and ethics
- Knowledge of analysis and design methodologies and techniques
Section 5: Web Resources
Good links:
- What do computer systems analysts do?
- What does a systems analyst do?
- Roles and responsibilities of a system analyst
Decent links:
Software Engineering Videos:
Systems Analysis and Design Videos: