Section 0: Module Objectives or Competencies
| Course Objective or Competency |
|---|
| The student will be able to write basic PHP applications in order to connect to and manipulate a database using PHP. |
Section 1: Overview
PHP, like any other programming language, provides facilities that enable you to affect the flow of control.
- That is, the language contains special statements that you can use to deviate from the sequential execution order.
Such statements are called control structures.
Some of the material in this section came from this chapter.
Section 2: Selection
Like JavaScript, PHP provides single selection, double selection, and multiple selection structures.
In fact, the syntax looks very much like that of JavaScript.
if Statement
This control structure lets us tell PHP to execute a set of statements only if some condition is met.
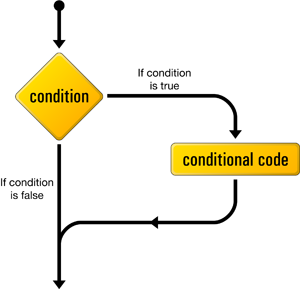
Here's what an if statement looks like in PHP code:
if (condition)
{
// conditional code to be executed if
condition is true
}
if-else Statement
This control structure lets us tell PHP to execute a set of statements if some condition is met, or a different set of statements if the condition is not met.
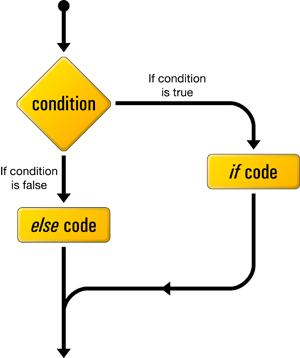
Here's what an if-else statement looks like in PHP code:
if (condition)
{
// conditional code to be executed if
condition is true
}
else
{
// conditional code to be executed if
condition is false
}
switch Statement
This control structure can be used in place of an if statement with multiple else if clauses in which one expression is tested for equality with several values.
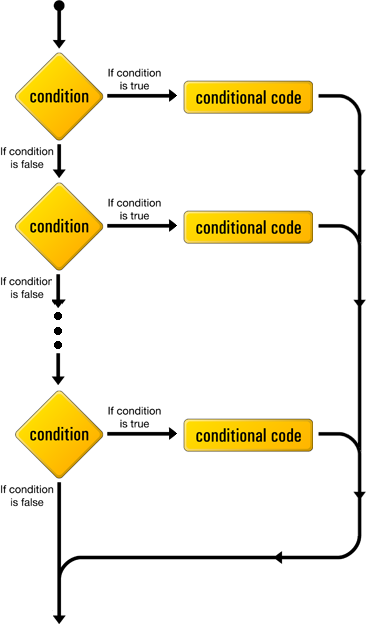
Here's what a switch statement looks like in PHP code:
switch (expression)
{
case label₁:
// conditional code to be executed if condition₁ is true
break;
case label₂:
// conditional code to be executed if condition₂ is true
break;
case labelₓ:
// conditional code to be executed if conditionₓ is true
break;
default:
// default code to be executed if no conditions are satisfied
}
The values in the case label may be literal values or expressions.
Section 3: Iteration
Again, like JavaScript, PHP offers pre-test (while) loops, post-test (do-while) loops, and count-controlled (for) loops.
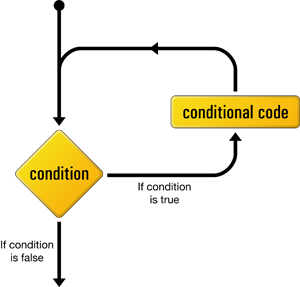
while
This control structure tells PHP to execute a set of statements as long as the condition is true.
Here's what a while statement looks like in PHP code:
while (condition)
{
// statement(s) to execute repeatedly as long as condition is true
}
The while loop works a lot like an if statement.
- The difference arises when the condition is true and the statement(s) are executed; instead of continuing the execution with the statement that follows the closing brace the condition is checked again.
- If the condition is still true, then the statement(s) are executed a second time, and a third, and will continue to be executed as long as the condition remains true.
- As soon as the condition evaluates false (whether it's the first time it's checked, or the ten thousandth), the execution jumps immediately to the statement that follows the while loop, after the closing brace.
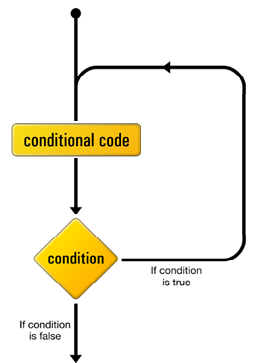
do-while
The do-while loop is similar to the while loop except that the conditional expression is tested at the end of the loop.
- As a result, the code inside the loop is always executed at least once.
Here's what a do-while statement looks like in PHP code:
do
{
// statement(s) to execute repeatedly
as long as condition is true
}
while (condition);
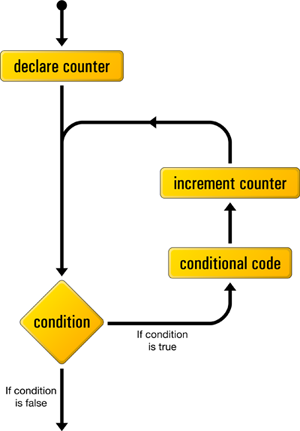
for
As you know, count-controlled loops count through a series of values until some condition is met.
Here's what a for statement looks like in PHP code:
for (counterDeclaration; condition; counterUpdate)
{
// statement(s) to execute repeatedly
as long as condition is true
}