Section 0: Module Objectives or Competencies
| Course Objective or Competency | Module Objectives or Competency |
|---|---|
| The student will develop an awareness of and be able to discuss the complexities of requirements determination. | Students will be able to list and explain what requirements determination entails, how difficult it is, and the importance of doing it correctly. |
| The student will be able to explain, assess, and apply a variety of requirements determination techniques including interviewing, observation, questionnaires, document analysis, and prototyping. | |
| Students will be able to list and explain some of the sources used in requirements determination. | |
| Students will be able to list and explain some of the prerequisites that must be met before undertaking requirements determination. | |
| Students will be able to list and explain and be prepared to avoid some of the problems that can be encountered during requirements determination. | |
| Students will be able to list and explain some of the deliverables produced by requirements determination. |
Section 1: Overview
Requirements determination:
- the last step in the Planning phase (or the first step in the Analysis phase)
- the process of communicating actions, facts, feelings, interpretations, and plans (schedules, activities, etc.) regarding a system
- the collection of information necessary to understand and model the existing system and the future system
- heavily involves users, and therefore requires a great deal of personal contacts and communication
- requires 30% of the analysis time
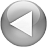
The importance of requirements determination.
Essential Systems Analyst Characteristics
- inquisitiveness – question everything
- impartiality – consider all issues to find the best organizational solution
- willingness to relax constraints – assume anything is possible
- attention to details – every fact must fit
- creative – challenge yourself to consider new approaches
Why Requirements Gathering is Critical
Scenario 1a: vs.
Scenario 1b:
Scenario 2a: vs.
Scenario 2b:
Section 2: Requirements Determination Techniques
- Reading and studying written materials.
- Observing is best suited to understanding human or machine processes that currently exist (passive participation).
- Participating is an advanced form of observing in which the data gatherer actually performs the activity (active participation).
- Surveying and questionnaires are best for written responses, and are used in situations where a small amount of data is needed from a large number of people.
- Interviewing provides a verbal response, and is a good method for collecting data on feelings and interpretations. It is the most widely used, and often most poorly used, technique.
- Brainstorming is used in group interviews as a means of arriving at new ideas. It is good in undefined situations in which no solution is evident. (Not barnstorming.)
Section 3: Sources for Requirements Determination
- Internal Sources
- Written documents
- People
- External Sources
- Textbooks
- Professional journals
- External documents (government regulations, etc.)
Section 4: Prerequisites to Requirements Determination
- Sanctioned by the group where you collect data?
- Management, unions, etc. must understand your purpose.
- Participants aware of your process and intentions?
- People have to know why you are there.
- Familiar with the subject?
- Read up on the subject and prepare — prior preparation prevents poor performance.
- Selected data gathering techniques?
- What's best for this situation and environment?
Section 5: Problems of Requirements Determination
- Approaching the wrong people
- Must find the right people from management directions
- Biasing the system or person by being there
- Your presence affects observation of the existing system.
- In interviews people say what they think they should.
- People telling you what they want you to hear
- People often give a biased view of their own, rather than a realistic assessment.
- Not sensing all the stimuli that are presented
- We perceive things selectively, and might miss some stimuli.
- Not interpreting correctly the things you sense
- Do you understand the jargon being used?
- Did you understand all that was being said?
- Not uncovering feelings or intentions
- User's feelings can influence the use or acceptance of a system.
Section 6: Deliverables for Requirements Determination
The major deliverable from requirements determination is the Requirements Specification.
- From interviews and observations – interview transcripts, observation notes, meeting minutes
- From existing written documents – mission and strategy statements, business forms, procedure manuals, job descriptions, training manuals, system documentation, flowcharts
- From computerized sources – Joint Application Design session results, CASE repositories, reports from existing systems, displays and reports from system prototype
Section 7: Interviewing
Interviewing is one of the primary ways analysts gather information about an information systems project.
Interview preparation may require the following:
- Reading background material
- Establishing interview objectives
- Deciding whom to interview
- Deciding on question types and structure
Question Types
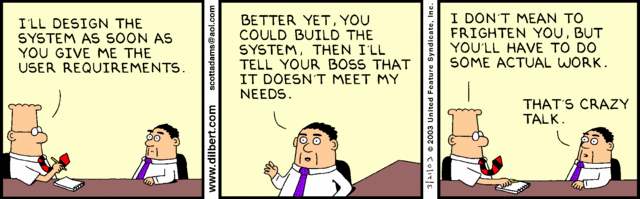
- Open-ended questions
- questions that have no pre-specified answers but rather leave all possible response options open to the respondent
- allow interviewees to respond how they wish, and to what length they wish
- well-suited to situations in which it is necessary to solicit opinions about some aspect of the system
- appropriate when the analyst is interested in breadth and depth of reply
- good when it is impossible to list effectively all possible responses to questions
- useful in exploratory situations in which analyst is not able to determine exactly what problems exist with a system – responses can be used to focus on cited problems more narrowly via interviews
- require that you anticipate the type of response that you will get because you must be able to correctly interpret responses
- must be narrow enough to guide respondents to
answer in specific way
- approach: phrase questions in context of satisfaction vs. dissatisfaction with current system
- approach: suggest some system features to prompt respondents to recall features of interest
- Advantages:
- Puts the interviewee at ease
- Allows the interviewer to pick up on the interviewee’s vocabulary
- Provides richness of detail
- Reveals avenues of further questioning that may have gone untapped
- Provides more interest for the interviewee
- Allows more spontaneity
- Makes phrasing easier for the interviewer
- Useful if the interviewer is less prepared
- Disadvantages:
- May result in too much irrelevant detail
- Possibly losing control of the interview
- May take too much time for the amount of useful information gained
- Potentially seeming that the interviewer is unprepared
- Possibly giving the impression that the interviewer is on a "fishing expedition"
- Closed-ended questions
- questions that ask those responding to choose from among a set of specified responses
- limit the number of possible responses
- appropriate for generating precise, reliable data that is easy to analyze
- useful when it is possible to list effectively all possible responses to questions and when all responses listed are mutually exclusive (choosing one precludes all others)
- useful when sampling large groups of people (easier to interpret)
- the methodology is efficient, and it requires little skill for interviewers to administer
- Advantages
- Saving interview time
- Easily comparing interviews
- Getting to the point
- Keeping control of the interview
- Covering a large area quickly
- Getting to relevant data
- Easier for the interviewer to analyze
- Disadvantages
- Boring for the interviewee
- Failure to obtain rich detail
- Missing main ideas
- Failing to build rapport between interviewer and interviewee
-
Attributes of Open-Ended and Closed Questions
- Bipolar Questions
- Bipolar questions are those that may be answered with a "yes" or "no" or "agree" or "disagree."
- Bipolar questions should be used sparingly
- A special kind of closed question
- Probes (Follow-ups)
- Probing questions elicit more detail about previous questions
- The purpose of probing questions is:
- To get more meaning
- To clarify
- To draw out and expand on the interviewee's point
- May be either open-ended or closed
Question Arrangement
There are three ways of arranging questions: pyramid, funnel, and diamond.
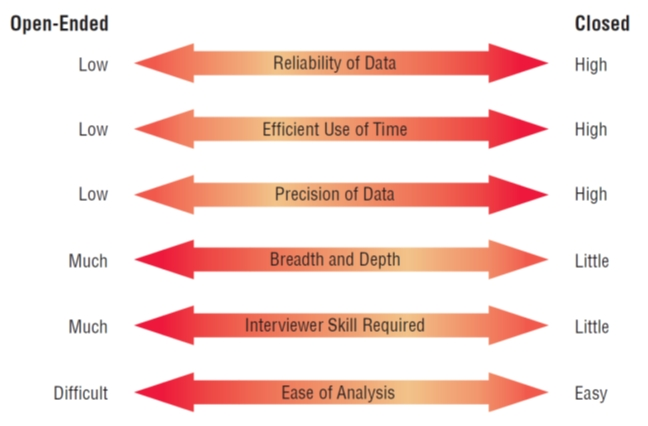
- Pyramid
- Begins with very detailed, often closed questions
- Expands by allowing open-ended questions and more generalized responses
- Is useful if interviewees need to be warmed up to the topic or seem reluctant to address the topic
-
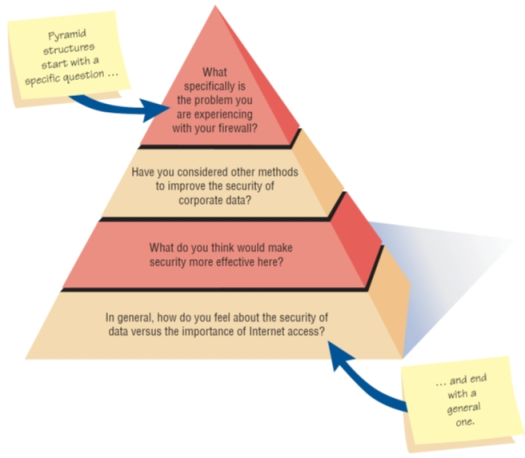
Pyramid Structure for Interviewing Goes from Specific to General Questions
- Funnel
- Begins with generalized, open-ended questions
- Concludes by narrowing the possible responses using closed questions
- Provides an easy, nonthreatening way to begin an interview
- Is useful when the interviewee feels emotionally about the topic
-
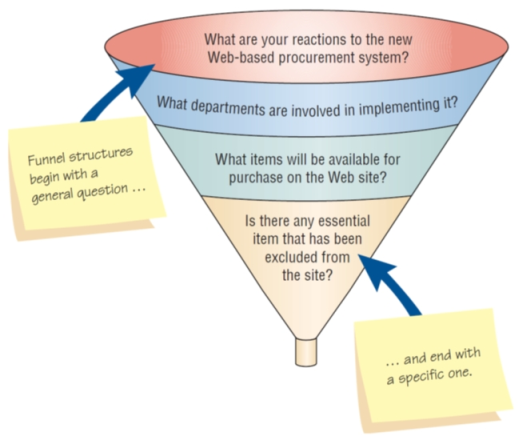
Funnel Structure for Interviewing Begins with Broad Questions then Funnels to Specific Questions
- Diamond
- A diamond-shaped structure begins in a very specific way.
- Then more general issues are examined
- Concludes with specific questions
- Combines the strength of both the pyramid and funnel structures
- Takes longer than the other structures
-
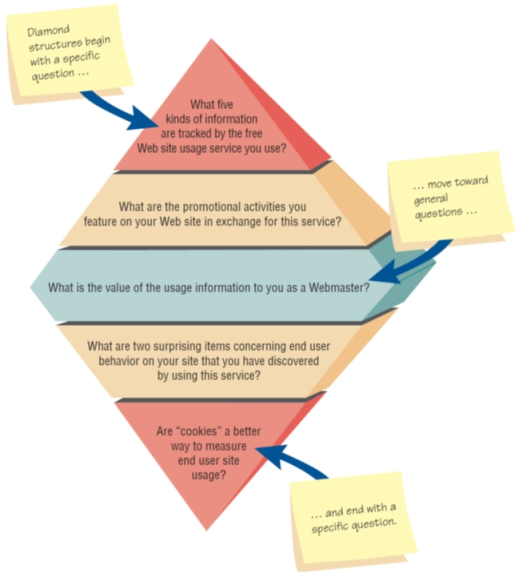
Diamond-Shaped Structure for Interviewing Combines the Pyramid and Funnel Structures
Guidelines for Effective Interviewing
- Plan the interview
- Prepare interviewee: appointment, priming questions.
- Prepare agenda, checklist, questions.
- Listen carefully and take notes and/or make an audio recording if permitted.
- Review notes within 48 hours.
- Be neutral.
- Seek diverse views. (example)
Drawbacks to individual interviews
- Contradictions and inconsistencies between interviewees
- Follow-up discussions are time consuming
- New interviews may reveal new questions that require additional interviews with those interviewed earlier
Here is a useful document on interviewing.
Section 8: Interviewing Groups
Joint Application Design
Joint Application Design (JAD) can replace a series of interviews with the user community.
- JAD is a technique that allows the analyst to accomplish requirements analysis and design the user interface with the users in a group setting.
- Conditions that support the use of JAD
- Users are restless and want something new.
- The organizational culture supports joint problem-solving behaviors.
- Analysts forecast an increase in the number of ideas using JAD.
- Personnel can be spared from their jobs for the length of time required.
- JAD Participants
- Session Leader: facilitates group process
- Users: active, speaking participants
- Managers: active, speaking participants
- Sponsor: high-level champion, limited participation
- Systems Analysts: should mostly listen
- Scribe: record session activities
- IS Staff: should mostly listen
- Benefits of JAD
- Time is saved, compared with traditional interviewing
- Rapid development of systems
- Improved user ownership of the system
- Creative idea production is improved
- Drawbacks of Using JAD
- JAD requires a large block of time to be available for all session participants.
- If preparation or the follow-up report is incomplete, the session may not be successful.
- The organizational skills and culture may not be conducive to a JAD session.
- End Result
- Documentation detailing existing system
- Features of proposed system
Nominal Group Technique
Nominal Group Technique (NGT) is a facilitated process that supports idea generation by groups.
- NGT is used to complement group meetings or as part of JAD effort.
- Process
- Members come together as a group, but initially work separately.
- Each person writes ideas.
- Facilitator reads ideas out loud, and they are written on a blackboard or flipchart.
- Group openly discusses the ideas for clarification.
- Ideas are prioritized, combined, selected, reduced.
Section 9: Observation
Observation involves watching users do their jobs and is best suited to understanding processes that currently exist.
- Sometimes referred to as passive participation.
- Observation provides insight on what organizational members actually do, not just what is documented or explained.
- Helps to obtain more firsthand and objective measures of employee interaction with information systems and can reveal important clues regarding HCI (Human/Computer Interaction) concerns.
- Allows you to see firsthand the relationships that exist between decision makers and other organizational members.
- Helps to confirm or negate conclusions resulting from other data gathering methods.
Guidelines
- decide which activities are to be observed
- decide the level of detail necessary
- create categories that adequately capture key activities
- prepare appropriate scales, checklists, or other materials for observation
- decide when to observe
Downside
- Can cause people to change their normal operating behavior. (link)
- Time-consuming and limited time to observe (snapshot).
Techniques
- Time Sampling – allows the analyst to set up specific intervals at which to observe activities.
- Event Sampling – allows the sampling of entire events rather than random time periods, and provides for observation of an integral behavior in its natural context.
- Best to utilize both.
-
Comparison of Time and Event Sampling Time Sampling Event Sampling Advantages - reduces bias when observations are randomized
- allows a representative view of frequent activities
- allows observation of actual behavior as it occurs
- allows observation of important events
Disadvantages - data gathering is fragmented with no time for decision to unfold
- misses infrequent but important decisions
- requires a great deal of time
- misses a representative sample of frequent decisions
Participation
- Participating is an advanced form of observing in which the data gatherer actually performs the activity.
- Sometimes referred to as active participation.
Section 10: Questionnaires
Questionnaires are special-purpose documents that allow analysts to collect information and opinions from respondents
- used to ascertain attitudes, beliefs, behaviors, and characteristics of several key people in an organization who may be affected by the current and proposed systems.
Reasons to Use Questionnaires
- people to be questioned are widely dispersed
- large number of people are involved
- important to determine proportion that supports or opposes change
- trying to gauge overall opinion before undertaking project
Characteristics of Questionnaires
- questionnaires require extensive planning
- questions must be transparently clear
- flow of questions must be presented in a way that brings out pertinent points
- respondents' questions must be anticipated and accounted for
- administration of the questionnaire must be planned in detail
Question Types
- Same as in interviews.
Guidelines for Choosing Language
- Use the language of respondents whenever possible. Keep wording simple.
- Be specific rather than vague in wording. Also avoid overly specific questions.
- Keep questions short.
- Do not talk down to respondents through low-level language choices.
- Avoid bias and objectionable questions.
- Target questions to the right respondents.
- Include only technically accurate questions.
- Use appropriate text for the reading level of the respondent.
Designing the Questionnaire
- Allow ample white space
- Allow ample space to write or type in responses
- Make it easy for respondents to clearly mark their answers
- Be consistent in style
Order of Questions
- Place most important questions first
- Cluster items of similar content together
- Introduce less controversial questions first
Methods of Administering the Questionnaire
- Convening all concerned respondents together at one time
- Personally administering the questionnaire
- Allowing respondents to self-administer the questionnaire
- Mailing questionnaires
- Administering over the Web or via email
Scales
- Details here.
Section 11: Document Analysis
Document analysis is the review of existing business documents in order to gain a historical and "formal" view of system requirements.
Types of information to be discovered
- Problems with existing system
- Opportunity to meet new need
- Organizational direction
- Names of key individuals
- Values of organization
- Special information processing circumstances
- Reasons for current system design
- Rules for processing data
Useful documents
- Written work procedures – describe how a particular job or task is performed, and often includes data and information used and created in the process.
- Business forms – explicitly indicate what data flow in and out of a system and data necessary for the system to function.
- Reports – the primary output of current system enables you to work backwards from the report to the data needed to generate it.
- Description of current information system – provides details of the existing system.
Formal vs. Informal
When analyzing documents, keep in mind the difference between formal and informal procedures.
- Formal Systems – the official way a system works as described in organizational documentation, such as work procedures.
- Informal Systems – the way a system actually works as discovered in interviews, observations, etc.
Section 12: Prototyping
Requirements determination
- Quickly converts requirements to working version of system.
- Once the users see requirements converted to system, they will ask for modifications or will generate additional requests.
Most useful when:
- User requests are not clear.
- Few users are involved in the system.
- Designs are complex and require concrete form.
- There is a history of communication problems between analysts and users.
- Tools are readily available to build prototype.
Drawbacks
- Tendency to avoid formal documentation.
- Difficult to adapt to more general user audience.
- Sharing data with other systems is often not considered.
- Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) checks are often bypassed.
More on prototyping here.
Section 13: Supplemental Reading
Section 14: Resources
-
Video: Requirements gathering
-
Video: Functional Requirements
-
Video: Requirements Gathering Process
-
Video: Requirement Gathering Techniques For A Business Analyst
-
Video: How to Collect Requirements for a Project
-
Video: Requirement Gathering in Software Engineering
-
Video: Requirement Elicitation Case Study - Real life example walk-through!
-
Video: How to Conduct a Requirements Gathering Interview
-
Video: Analysis and Requirements Gathering 1
-
Video: Requirement Prioritization Techniques
-
Video: Software Requirements Gathering